Electrical Stimulation is a physical therapy modality. By placing electrodes on the skin in various locations the doctor can recruit the appropriate muscle fibers. Contracting the muscle via electrical stimulation helps strengthen the affected muscle. The physical therapist can change the current setting to allow for a forceful or gentle muscle contraction. Along with increasing muscle strength, the contraction of the muscle also promotes blood supply to the area that assists in healing.
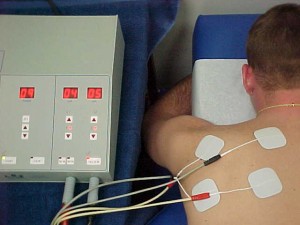 There are many forms of electric stimulation. We most frequently use interferential therapy. It is used to reduce pain, generate muscle fiber contraction and reduce swelling and inflammation as well as to reduce muscle spasm. It is often used in conjunction with either heat or ice.
There are many forms of electric stimulation. We most frequently use interferential therapy. It is used to reduce pain, generate muscle fiber contraction and reduce swelling and inflammation as well as to reduce muscle spasm. It is often used in conjunction with either heat or ice.
Electrical Muscle Stimulation or EMS may be used to strengthen muscle or prevent atrophy. This differs from a battery-operated TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) unit, which may be provided for home use to control pain, as it offers no curative value.